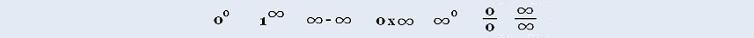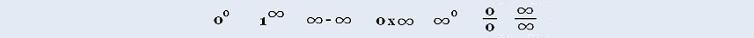Calculus I: Limits
Rules on the evaluation of limits :
1. Limits Properties
If lim f(x) = b and
x → a
|
lim g(x) = c
x → a
|
Then:
a)
lim k f(x) = k (
x → a
| (lim f(x)) = k b
x → a
|
b)
lim (f(x) ± g(x)) =
x → a
| lim f(x) ±
x → a
|
lim g(x) = b ± c
x → a
|
c)
lim f(x) g(x) =
x → a
| lim f(x) .
x → a
|
lim g(x) = b c
x → a
|
d)
lim f(x)/g(x) =
x → a
| lim f(x) /
x → a
|
lim g(x) = b /c (c≠0)
x → a
|
e)
lim (f(x))n =
x → a
| (lim (f(x)
x → a)n
|
= bn
|
f)
lim (f(x))1/n =
x → a
| (lim (f(x)
x → a)1/n
|
= b1/n
|
with n even integer and b > = 0 |
g)
If P(x) is a polynomial function of standard form
Σ an xn, we have:
lim P(x) = P(a)
x → a
2. Examples
2.1. Example 1
lim ( 3 - 4 x) = 3 - 4(- 5) = 3 + 20 = 23
x → - 5
2.2. Example 2
lim ( 13 - 4 x) = 13 - 4(5) = - 7
x → 5+
2.3. Example 3
lim 2 x2 - 2 x + 3
x → -1
lim 2 x2 - 2 x + 3 =
x → -1
| 2 lim x2 - 2 lim x + 3 = 7
x → -1
|
2.4. Example 4
lim 2 x2/(x - 5) = 2 (1)2/(1 - 5) = 2/(- 4) = - 1/2
x → 1
2.5. Example 5
lim (2 x + 5)6
x → - 5/2
lim (2 x + 5)6 =
x → - 5/2
| [lim (2 x + 5) = 06 = 0
x → - 5/2 ]6
|
2.6. Example 6
lim (2 x + 5)6
x → - 5/2
| (lim (2 x + 5) = 06 = 0
x → - 5/2 )6
|
2.7. Example 7
lim (x - 2)1/2
x → 2
lim (x - 2)1/2 
x → 2-
lim (x - 2)1/2 = 0
x → 2+
so
lim (x - 2)1/2 
x → 2
2.8. Example 8
| | | 3x2 + 1 | | x < 0 |
| f(x) = | | x - 1 | | 0 < x <= 3 |
| | | x + 1 | | x > 3 |
lim f(x) = 3 02 + 1 = 1
x → 0-
lim f(x) = 0 - 1 = - 1
x → 0+
lim f(x) ≠
x → 0-
| lim f(x)
x → 0+
|
Therefore:
lim f(x) 
x → 0
In addition: f(0) ∄
b)
lim f(x) = 3 - 1 = 2
x → 3-
lim f(x) = 3 + 1 = 4
x → 3+
lim f(x) ≠
x → 3-
| lim f(x)
x → 3+
|
Therefore:
lim f(x) 
x → 3
In addition: f(3) = 3 - 1 = 2
3. Exercises
1-
lim (2x - 3)
x → - 4
2-
lim (5 x )
x → 3
3-
lim (2 x + 7)
x → o+
4-
lim (x2 + 1)
x → - 1-
5-
lim 2(x - 4)3
x → - 1
6-
lim 2(x + 3)/(x - 1)
x → 2
7-
lim 7 (x2 - 3)/(x - √3)
x → (√3)-
lim 7 (x2 - 3)/(x - √3)
x → (√3)+
lim 7 (x2 - 3)/(x - √3)
x → √3
8-
P(x) = x3 - x - 4
lim P(x)
x → + 1
Remark P(x) is a
polynomial function, so
lim P(x) = P(a)
x → a

9-
lim 2(x3 + 3)/(x3 + 1)
x → 0
10-
lim (x3 + 3)3
x → -1
11-
lim [7 + (x2 - 1)1/2]/(x2 + 3 x + 1)5
x → 0
12-
lim √x
x → 0
13-
lim (x + 1 + (x - 1)2)
x → 1
Evaluate 1+ and 1-.
14-
| | | x2 - 1 | | x <= 0 |
| f(x) = | | x - 1 | | 0 < x <= 2 |
| | | x + 1 | | x > 2 |
lim f(x)
x → 0+
lim f(x)
x → 0-
lim f(x)
x → 2+
lim f(x)
x → 2-
lim f(x)
x → 4
|