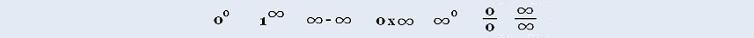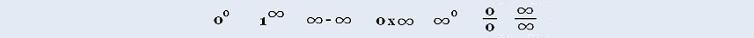Calculus I: Limits
Infinite limit and limit at infinity
1. Definitions
An infinite limit is written as:
lim f(x) = ∞
x → a
A limit at infinity is written as:
lim f(x) = b
x → ∞
2. Operations with - ∞ and + ∞
a is a real constant, and n is a
positive integer.
addition and
subtraction
∞ + ∞ = ∞
-∞ - ∞ = -∞
∞ + a = ∞
-∞ + a = -∞
∞ - a= ∞
-∞ - a = -∞
|
multiplication
∞ . ∞ = ∞
∞ . (-∞ ) = -∞
(-∞ ) . (∞ ) = -∞
a . ∞ = ∞
a . (-∞ ) = -∞
(- a) . ∞ = -∞
(- a) . (-∞ ) = ∞
|
division
�c/∞ = 0
�c/ - ∞ = 0
∞/a = ∞
- ∞/a = -∞
∞ /(- a) = -∞
-∞/(- a) = ∞
1/0+ = + ∞
1/0- = - ∞
|
power and exponents
(∞)1/n = ∞
(-∞)1/n even doesn't exist
(-∞)1/n odd = - ∞
(∞)n = ∞
(-∞)n even = ∞
(-∞)n odd = - ∞
(∞)0 Undetermined
|
2. Examples
2.1. Example 1
lim ( 4 x3 - x + 1)
x → - ∞
= lim 4 x3 - lim x + 1 =
4 lim x3 - lim x + 1 = - ∞ - ∞ = - ∞
x → - ∞
2.2. Example 2
lim (x2 + 2x + 1)/( x + 1) = ∞/∞ Undetermined
x → + ∞
2.3. Example 3
lim (x2 + 2x + 1)/( x + 1) = ∞/∞ Undetermined
x → - ∞
2.4. Example 4
lim 1/( x + 1) = 1/ 0- = - ∞
x → - 1-
lim 1/( x + 1) = 1/ 0+ = + ∞
x → - 1+
so
lim 1/( x + 1) 
x → - 1
2.5. Example 5
lim 1/( x + 1)2 = 1/ 0+ = + ∞
x → - 1-
lim 1/( x + 1)2 = 1/ 0+ = + ∞
x → - 1+
so
lim 1/( x + 1)2 = + ∞
x → - 1
3. Exercises
a)
lim (3x2 - 6x + 1)
x → - ∞
b)
lim x(- 3x + 4)
x → - ∞
c)
lim ( 3 - x)1/2
x → - ∞
d)
lim (1/x)
x → - ∞
e)
lim (1/x)
x → + ∞
f)
lim (1/x)
x → 0+
g)
lim (1/x)
x → 0-
h)
lim (1/x)
x → 0
i)
lim (1/x2)
x → 0-
j)
lim (1/|x|)
x → 0
k)
lim ((x - 3)/x2(x4 + 2))
x → 0
l)
lim (1/(x - 3)2)
x → 3
m)
lim (2/(x - 3)3)
x → 3
n)
lim ((1 - x)/(x - 7)2)
x → 7
o)
lim (8x/(x - 7)1/2)
x → 7
|