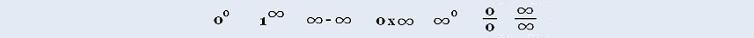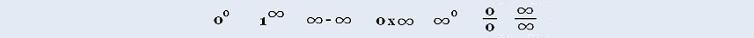Calculus I
Limits
Derivative
Exercices
Applications
Marginal analysis
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
Calculus I: Optimization
What are the dimensions of a rectangle we want to
construct with a wire of length L, to maximize its area?
This king of problems involving extrema are called optimization problems.
Generally, they are solved by setting two equations. One is the "constraint" equation and the other is the "optimization" equation.
The first is used to solve for one of the variables. The result is then substituted into the second equation. We may have 0, 1, or more constraint equations.
The obtained built second equation is the function to optimize.
So from a proposed word problem, we set up a function to
be differentiated and solved for the needed extrema.
The optimization is a step-by-step procedure that uses derivatives.
1. Optimization problems: the procedure
-
Since these kind of problems are word problems, it is essential to
know exactly what the problem is asking and understand it by reading slowly and carefully, several times if needed before trying to solve it.
What are the given quantities? What are the unknowns?
-
When it is appropriate, sketch a graph or draw a diagram or a picture
of the problem.
-
Define the variables to be used and label the picture or diagram with these variables. This step helps to set up the mathematical equations.
-
Write down the two equations: the "constraint" equation and the "optimization" equation. Express the optimization" equation as a function of only one variable,
and, if it is needed, reduce it to be easily differentiable.
-
Differentiate the function. Generally, we need only
the first derivative.
-
Solve the mathematical problem, and give an answer in terms of
the given subject.
-
Verify the result, and whether the solution makes sense for the given questions.
-
It is useful to set the behavior of the function f(x)
to optimize: Continuity of some points, variation-sign table, and
graph.
2. Examples:
Example 1:
What are the dimensions of a rectangle we want to
construct with a wire of length L, to maximize its area?
-
We are searching for the dimensions of a rectangle that are
the unknown quantities.
The given quantity is the length of the wire that will
constitute the perimeter of the rectangle we want to built.
-
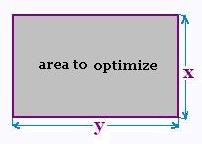
-
The variables are x and y. x is the width and
y is the length of the rectangle.
-
The two equations:
Constraint equation: 2 x + 2 y = L
Optimization equation: A = x y
A = x y = x (L - 2 x)/2 = - x2 + (L/2) x = f (x)
-
f '(x) = - 2 x + (L/2)
-
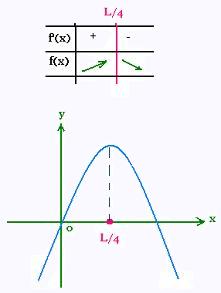
To optimize f(x), we set f '(x) = 0. That is
- 2 x + (L/2) = 0 , that gives
x = L/4
Therefore
y = L/4
-
The rectangle we want to built is a square of side L/4.
Example 2:
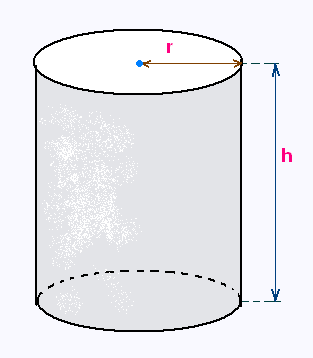
A manufacturer needs to make a cylindrical can that will hold C liters of liquid. Determine the dimensions of the can that will minimize the amount of material used in its construction.
Solution
In this problem the constraint is the volume and we want
to minimize the amount of material used. This means that what we
want to minimize is the total surface area of the can.
The equations for the volume and surface area of a cylinder are
V = π r2 h (1)
A = 2π r h + 2π r2 (2)
Constraint: V = π r2 h = C
Minimize: A = 2π r h + 2π r2
h from (1) in (2) gives A(r)
We get the first derivative of A(r) and equal it to zero
We find r then h.
Example 3:
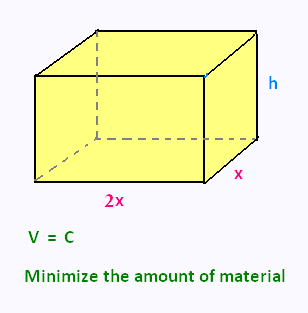
We need to make a prism rectangular box that will hold V liters of sand. Determine the dimensions of the box that will minimize the amount of material used in its construction.
3. Exercises
Recall the main steps to optimization:
1. Read the problem,
2. Reread the problem,
3. Draw a picture if appropriate,
4. Identify the variables,
5. Identify the constants,
6. Set constraints,
7. Draw the related graph or picture,
8. Determine what quantity needs to be maximized or minimized,
9. Find an appropriate equation for what needs to be
maximized or minimized, and reduce it to one variable,
10. Find the derivative and critical points for that equation,
11. Test the found results,
12. Reread the question and make sure you have answered what was asked.
|
|