Nuclear Physics
The nucleus
Radioactivity
Applications
Particle accelerators
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
Nuclear Physics &
Particle Physics
Particle accelerators
Electrostatic Accelerators
Van de Graaff Accelerator
Van de Graaff Accelerator
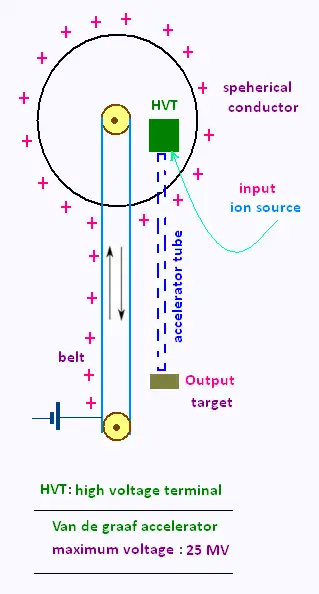
The Van de Graaf generator is a machine for producing extremely high potential
differences.
It is an electrostatic generator which uses a moving belt to accumulate electric charge. It may produce anywhere from 200 Kvolts to many megavolts, depending on size.
R. J. Van de Graaff built the Van de Graaff accelerator in 1929. In this
machine a high potential difference is built up and maintained on a conducting surface
by the continuous transfer of positive static charges from a moving belt to the surface.
When used as a particle accelerator, an ion source is located inside the high-voltage
terminal. Ions are accelerated from the source to the target by the electric voltage between the high-voltage supply and ground.
The maximum energy obtainable from an electrostatic accelerator such as the Van de Graaff can be greatly increased by the application of the "tandem" principle.
 Robert Jemison Van de Graaff est un physicien américain. Il est né le 20 décembre 1901
et mort le 16 janvier 1967. Il est est à l'origine de la machine électrostatique
qui porte son nom.
Robert Jemison Van de Graaff est un physicien américain. Il est né le 20 décembre 1901
et mort le 16 janvier 1967. Il est est à l'origine de la machine électrostatique
qui porte son nom.
Van de Graaff obtient, en 1923, le titre de Master of Science à l'université d'Alabama.
Après un séjour à la Sorbonne, en France entre 1924 et 1925, il obtient son titre de
docteur en sciences à Oxford en 1928. En 1929, il retourne aux États-Unis,
au laboratoire de physique de Palmer à l'université de Princeton.
En son hommage, on a donné son nom au cratère Van de Graaff sur la
face cachée de la Lune en 1970
|
|