Nuclear Physics
The nucleus
Radioactivity
Applications
Particle accelerators
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
Nuclear Physics &
Particle Physics
Particle accelerators
PET/CT Scanning
1. Radioisotopes
The cyclotron produces radioisotopes. radioisotope
is an atom whose nucleus is radioactive. Nuclear reactors allow
also the production of radioisotopes, but in larger amounts, with a cost
weaker.
This machine uses the bombardment of a target with neutrons which cause
fission reactions. The radioisotopes are produced locally in hospitals. when
will be transported, they must have a long period.
Nuclear reactors produce many gamma emitters and all radionuclides
used in therapy. It is the case of fluorine-18 and molybdenum-99.
Radioactive isotopes are, in specific cases, detectable using
devices such as the gamma camera or positron emission
tomography.
Radioactive atoms are detectable when issued
radiation γ . For example, fluorine-18 decays by
proces:
18 9 F → 188O + p+
p + → n + e+ + ν e
e + + e- → γ + γ
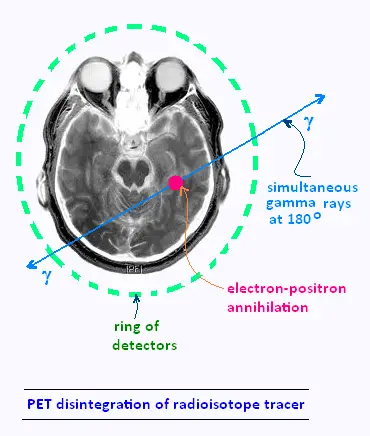
It is, therefore, necessary to choose radionuclides that emit mainly
gamma rays, radiation that radiates little and penetrating enough to get out
the organism and to be detected.
The period of the radioisotope must be long enough to allow
following the biological process studied and proceed with the examination but also be
short enough to avoid unnecessary irradiation.
Technetium-99m is the most widely used radioisotope (80% to 90% of Scintigraphic
examinations) because it allows the exploration of many parts of the body
and only emits gamma including energy (140 keV) , which is very well suited
detectors gamma cameras.
Radioisotopes positron emitters are also used for the "Positron emission",
for radiotherapy metabolic. beta-less transmitters are used to deliver locally
dose to the target tissue.
2. Tracers
Tracers are generally radiopharmaceuticals
that incorporate in their formula a radioisotope.
This radioactive nucleus is called label .
A tracer, or radiotracer can be a single radioactive atom . This is the case of gas
nobles used for lung scans: krypton-81m or xenon-133.
A tracer can be also a a labeled molecule with an isotope.
This isotope has to be chemically attached to the molecule without modifying properties
thereof. The binding should be strong so that the radioactive element will
not lost along the way, in which case it would follow the path of the element
radioactive and not that of the molecule of interest.
The examination comprises administering to the patient a radioactive tracer, selected
based on its ability to monitor metabolism or provide a diagnosis of the
operation of a given organ.
This is the issue that atom by radiation which tracks to
traces the journey of this tracer in the living.
The "radiopharmaceuticals" products containing labeled molecules by
a radioactive isotope are generally administered intravenously.
They are also administered by inhalation.
The examination comprises administering to the patient a radioactive tracer, selected
according to its capacity to monitor metabolism or provide a diagnosis of the operation
of a given organ.
With these radioactive isotopes, it is possible to keep track of an atom or
a chemical species without disturbing the physical, chemical or biological behavior.
2. Medical imaging
 Positron emission tomography (PET) is an imaging examination in nuclear medicine
which employs a form of radioactive sugar to create images of body functions and
metabolism.
Positron emission tomography (PET) is an imaging examination in nuclear medicine
which employs a form of radioactive sugar to create images of body functions and
metabolism.
PET imaging is used to assess the biological function of cells and organs, whether
normal or abnormal.
PET uses radiopharmaceutical product made of a radioisotope attached to a natural compound
of the body, usually glucose. This product is concentrated in certain areas of the body and
is detected by the PET scanner.
The PET scanner consists of sensors that form a circle. These detectors record the radioactivity
distribution pattern emitted by the radiopharmaceutical in the body. A computer analyzes the
distribution patterns and product images in 3 dimensions and color of the examined area.
Different colors or various degrees of gloss on a plate representing the different function
levels of a tissue or organ.
PET scanners are expensive both to buy that operation, so they are not easily available
and usable. PET is only available in a very limited number of centers in Canada.
|
|