Quantum Mechanics
Schrodinger equation
Quantum Mechanics
Propagators : Pg
Quantum Simple Harmonic
Oscillator QSHO
Quantum Mechanics
Simulation With GNU Octave
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
|
elliptic coordinates
Quantum Mechanics enables us to understands the existence and properties of chemical bonds
that are responsible for the formation of molecules from isolated atoms. The simplest molecule possible is the H2+ ion, which is composed of two protons and a single electron.
ρ = R/ao
ρ1= r1/ao
ρ2= r2/ao
R is the internuclear distance P2 nad P2
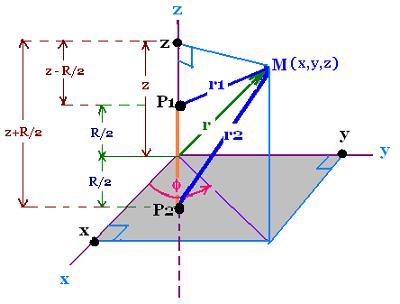
The normalized gound state wave function 1s of the hydrogen atom formed around P1 is:
φ1 = 1/(πao3)1/2
exp{- ρ1}
It is convenient to use the system
of elliptic coordinates. The point Mof space (electron) is defined by:
μ = (r1 + r2)/R = (ρ1 + ρ2)/ρ
ν = = (r1 - r2)/R = (ρ1 - ρ2)/ρ
r12 = x2 + y2 + (z - R/2)2
r22 = x2 = Y2 = (z + R/2)2
tan φ = y/x
We will calculate the Jacobian of the transformation: {x,y,z} → {μ, ν, φ}; in order to write:
d3r = dxdydz = J dμdνdφ
It is more easy to calculate first J-1, then set J according to JJ-1 = 1.
Therefore:
∂μ/∂x = (1/R) (∂r1/∂x + ∂r2/∂x ) =
(1/R) (x/r1 + x/r2) = μx/r1r2
∂ν/∂x = (1/R) (∂r1/∂x - ∂r2/∂x ) =
(1/R) (x/r1 - x/r2) = - νx/r1r2
∂μ/∂y = μy/r1r2
∂ν/∂y = - νy/r1r2
∂μ/∂z = (1/R) (∂r1/∂z + ∂r2/∂z ) =
(1/R) ((z - R/2)r1 + (z + R/2)/r2) = (μz + νR/2)/r1r2
∂ν/∂z = (1/R) (∂r1/∂z - ∂r2/∂z ) =
(1/R) ((z - R/2)r1 - (z + R/2)/r2) = - (νz + μR/2)/r1r2
∂φ/∂x = - y/(x2 + y2)
∂φ/∂y = x/(x2 + y2)
∂φ/∂z = 0
Therefore:
J-1 = (1/(r1r2)2)
| μx μy μz + νR/2|
|- νx - νy - (νz + μR/2)|
|- y/(x2 + y2) x/(x2 + y2) 0|
= μx (νz + μR/2)(x/(x2 + y2))
+ μy (νz + μR/2)(y/(x2 + y2))
- (μz + νR/2) =
(R/2)(μ2 - ν2). Then:
J-1 = (R/2)(μ2 - ν2) (1/(r1r2)2)
Since
μ2 - ν2 =
4r1r2/R2, we have then:
(r1r2)2 = R4(μ2 - ν2)2/16
Hence:
J-1 = 8/R3(μ2 - ν2)
Then:
J = R3(μ2 - ν2)/8
Jacobian of the transformation:
{x,y,z} → {μ, ν, φ}:
d3r = dxdydz = J dμdνdφ
J = R3(μ2 - ν2)/8
<φ1,φ2 > =
∫∫ d3r φ1* (r)φ2 (r) = (1/πao3) ∫∫∫ d3r exp{-( r1 + r2)/ao}
= (1/πao3) ∫∫∫ J dμdνdφ exp{- μρ}
We have:
μ = (r1 + r2)/R
μmin = R/R = 1
μmax = ∞/R = ∞
And
ν = (r1 - r2)/R
νmin = -R/R = -1
νmax = R/R = 1;
Then:
<φ1,φ2 > =
(R3/8)(1/πao3) ∫∫∫
(μ2 - ν2) dμdνdφ exp{- μρ}
[μ: 1 → ∞, ν: -1 → +1, φ: 0 → 2π ]
=
2π(R3/8)(1/πao3)
∫∫(μ2 - ν2) dμdν exp{- μρ}
[μ: 1 → ∞, ν: -1 → +1,]
Using ρ = R/ao yields:
R3 = ρ3ao 3
= ρ3/4
∫ x2exp{- ax} dx = x2 (exp{- ax}/(-a)) -
∫ (exp{- ax}/(-a)) (2xdx) =
(- 1/a)x2 (exp{- ax}) +
( 2/a) ∫ x (exp{- ax}) dx
∫ x (exp{- ax}) dx = x ((exp{- ax})/(-a)) - ∫ ((exp{- ax})/(-a))dx =
-(x/a)(exp{- ax}) +(1/a) ∫ (exp{- ax})dx
=
-(x/a)(exp{- ax}) - (1/a2)(exp{- ax}) = - (exp{- ax}/a) [x + 1/a]
∫ x (exp{- ax}) dx = - (exp{- ax}/a) [ x + 1/a]
With a = 1:
∫ x exp{- x} dx = exp{-x} [ - x - 1]
Then:
∫ xexp{- ax} dx = -(x/a)(exp{- ax}) +(1/a) ∫ (exp{- ax})dx
∫ x2exp{- ax} dx =
(- 1/a)x2 (exp{- ax}) + (2/a) [-(x/a)(exp{- ax}) +(1/a) ∫ (exp{- ax})dx] =
(- 1/a)x2 (exp{- ax}) + (2/a) [-(x/a)(exp{- ax}) - (1/a2) exp{- ax}] =
(exp{- ax}/a) [- x2 - 2 [(x/a) + (1/a2)]]
∫ x2exp{- ax} dx = (exp{- ax}/a) (- x2 -2x/a - 2/a2)
<φ1,φ2 > =
ρ3/4[
∫ dμ exp{- μρ} ∫(μ2 - ν2) dν]
[μ: 1 → ∞, ν: -1 → +1,]
=
ρ3/4 [
∫ dμ exp{- μρ} (2μ2 - 2/3) ]
[μ: 1 → ∞]
=
ρ3/2 [
∫ dμ exp{- μρ} (μ2 - 1/3)]
[μ: 1 → ∞]
=
ρ3/2 [
∫ dμ exp{- μρ} μ2 - 1/3 ∫ dμexp{- μρ}]
[μ: 1 → ∞]
=
ρ3/2 [
(exp{- ρμ}/ρ) [- μ2 - 2 [(μ/ρ) + (1/ρ2)]]
+( 1/3ρ) exp{- μρ}]
[μ: 1 → ∞]
=
ρ3/2 [
(exp{- ρμ}/ρ) [- μ2 - 2 [(μ/ρ) + (1/ρ2)]
+ 1/3]]
[μ: 1 → ∞]
=
ρ3/2 [
(exp{- ρ}/ρ) [ 1 + 2 [(1/ρ) + (1/ρ2)]
- 1/3]]
=
ρ3/2
(exp{- ρ}/ρ) [2/3 + 2/ρ + 2/ρ2]
=
ρ2
(exp{- ρ}) [1/3 + 1/ρ + 1/ρ2]
=
exp{- ρ} (ρ2/3 + ρ + 1)
<φ1,φ2 > = exp(- ρ) (ρ2/3 + ρ + 1)
ρ = R/ao
--------------
I = ρ2EI ∫∫∫dμdν(μ + ν) exp{-(μ + ν)ρ} dφ
[μ: 1 → ∞, ν: -1 → +1, φ: 0 → 2π ]
Let's write:
x = ρμ and y = ρν
I = (EI/ρ) ∫∫dx;dy;(x + y) exp{-(x + y)}
[x: ρ → ∞, y: -ρ → +ρ ]
I = I = (EI/ρ) J
J = ∫∫dx;dy;(x + y) exp{-(x + y)} = ∫ exp{-(x} dx; ∫dy;(x + y) exp{- y}
[x: ρ → ∞, y: -ρ → +ρ ]
J = ∫ exp{-(x} dx; K
K = ∫dy;(x + y) exp{- y} = x ∫dy; exp{- y} + ∫dy;y exp{- y} =
[y: -ρ → +ρ ]
- x exp{- y} - y exp{- y} - exp{- y} = exp{- y}[ - x - y - 1}
[y: -ρ → +ρ ]
=
exp{- ρ}[ - x - ρ - 1} + exp{ ρ }[ x - ρ + 1 } =
= exp{- ρ}[ - x - ρ - 1} + exp{ ρ }[ x - ρ + 1 }
x(exp{ρ} - exp{- ρ}) - exp{- ρ}[ + ρ + 1] + exp{ ρ }[ - ρ + 1 ]
= x A + B
A = exp{ρ} - exp{- ρ}
B = - exp{- ρ}[ + ρ + 1] + exp{ ρ }[ - ρ + 1 ]
A + B = exp{ ρ }[- ρ + 1 + 1] - exp{- ρ}[ + ρ + 1 + 1] =
exp{ ρ }[- ρ + 2] - exp{- ρ}[ + ρ + 2]
J = ∫exp{-(x} dx; (xA + B)
[x: ρ → ∞,]
= A ∫exp{-(x} x dx; + B ∫exp{-(x}dx; =
[x: ρ → ∞]
A(- x exp{-x} - exp{-x}) - B exp{-(x} = exp{-(x} [- xA - A -B ]
[x: ρ → ∞]
= exp{-(ρ} [ρA + A + B]
=
exp{-(ρ} [ρ(exp{ρ} - exp{- ρ}) + exp{ ρ }[- ρ + 2] - exp{- ρ}[ + ρ + 2] ]
=
ρ(1 - exp{- 2ρ}) + [- ρ + 2] - exp{- 2ρ}[ + ρ + 2]
=
- ρexp{- 2ρ} + 2 - exp{- 2ρ}[ + ρ + 2] =
exp{- 2ρ} [- 2ρ - 2] + 2 = 2 [1 - (ρ + 1) exp{- 2ρ}]
Therefore:
I = (EI/ρ) 2 [1 - (ρ + 1) exp{- 2ρ}] =
(2EI/ρ) [1 - (ρ + 1) exp{- 2ρ}]
<φ1(r1)|e2/r2|φ1(r1) > = (2EI/ρ) [1 - (ρ + 1) exp{- 2ρ}]
x exp{-x} = x / exp{x}
lim x exp{-x} = ∞/∞ :indetermined.
x → + ∞
De l'Hopital theorem:
lim x exp{-x} = lim x / exp{x} = lim 1/ exp{x} = 0
x → + ∞
lim x exp{- x} = 0
x → + ∞
<φ1|e2/r1|φ2> =
e2 ∫∫∫ φ1*(r1)(1/r1) φ2(r2) d3r
We have:
φ1(r1)= (1/πao3)1/2exp{-ρ1}
φ2(r2)= (1/πao3)1/2exp{-ρ2}
r1 = ρ ao(μ + ν)/2
ρ = R/ao
∫dφ = 2π
ρ1 + ρ2 = μρ
J = [R3/8] (μ2 - ν2)
= [(ρ ao)3/8] (μ2 - ν2)
EI = e2/2ao
Therefore:
<φ1|e2/r1|φ2> =
e2 (1/πao3) [(ρ ao)3/8] (2/ρao) 2π
∫∫exp{-μρ} (1/(μ + ν))(μ2 - ν2) dμdν =
[μ: 1 → ∞, ν: -1 → +1]
(ρ)2EI
∫∫ exp{- μρ}(μ - ν) dμdν =
[μ: 1 → ∞, ν: -1 → +1]
(ρ)2EI
∫exp{- μρ}dμ ∫ (μ - ν) dν =
[μ: 1 → ∞, ν: -1 → +1]
=
(ρ)2EI
∫exp{- μρ}dμ (μ 2 - 0) =
[μ: 1 → ∞]
(ρ)2EI
2 ∫exp{- μρ}dμ = (2/ρ2)[- μρ - 1]exp{- μρ}
[μ: 1 → ∞]
=
(ρ)2EI
(2/ρ2)[ ρ + 1]exp{- ρ}
Hence:
<φ1|e2/r1|φ2> =
2EI [ρ + 1] exp{- ρ}
<φ1|e2/r1|φ2> =
2EI (ρ + 1) exp(- ρ)
|
|