Quantum Mechanics
Schrodinger equation
Quantum Mechanics
Propagators : Pg
Quantum Simple Harmonic
Oscillator QSHO
Quantum Mechanics
Simulation With GNU Octave
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
| Pauli matrices
Spin is an intrinsic angular momentum of any
rotating fundamental particles as an electron within
an atom.
S = Sx i + Sy j + Sz k
S2 = S2x + S2y + S2z
The two possible spin states are |s m> are
|1/2 1/2> and |1/2 -1/2> .
We use the following notations:
|0> or |↑> for |1/2 1/2>, and
|1> or |↓> for |1/2 -1/2>
|0> and |1> are simultaneous eigenvectors
of S2 and Sz. Therefore
S2|0> = (1/2) (1/2 + 1)ℏ2|0>
S2|1> = (1/2) (1/2 + 1)ℏ2|1>
Sz|0> = (1/2) ℏ|0>
Sz|1> = (-1/2) ℏ|1>
S2|0> = (3/4)ℏ2|0>
S2|1> = (3/4)ℏ2|1>
Sz|0> = (1/2)ℏ|0>
Sz|1> = (-1/2)ℏ|1>
The matrix for Sz in ℏ/2 units is:
|1 0|
|0 -1|
We have also:
Sx = (1/2)(S+ + S-)
Sy = (1/2i)(S+ - S-)
So
S+ |s m> = [s(s+1) -m(m+1)]1/2ℏ |s m+1>
S= |s m> = [s(s+1) -m(m-1)]1/2ℏ |s m-1>
Thus:
S+ |0> = 0
S+ |1> = ℏ |0>
S- |0> = ℏ |1>
S- |1> = 0
Therefore:
Sx11 = <0|Sx|0> =
<0|(1/2)(S+ + S-)|0> = (1/2)<0|S+|0> + (1/2)<0|S-|0>
(1/2)<1|S+|1> + (1/2)<1|S-|1> = 0 + 0 = 0
Sx22 = <1|Sx|1> =
<1|(1/2)(S+ + S-)|1> = (1/2)<1|S+|1> + (1/2)<1|S-|1>
(1/2)<1|S+|1> + (1/2)<1|S-|1> = 0 + 0 = 0
Sx12 = <0|Sx|1> =
<0|(1/2)(S+ + S-)|1> = (1/2)<0|S+|1> + (1/2)<0|S-|1>
(1/2)<0|S+|1> + (1/2)<0|S-|1> =ℏ/2 + 0 = ℏ/2
Sx21 = <1|Sx|0> =
<1|(1/2)(S+ + S-)|0> = (1/2)<1|S+|0> + (1/2)<1|S-|0>
(1/2)<1|S+|1> + (1/2)<1|S-|1> = 0 + ℏ/2 = ℏ/2
The matrix for Sx in ℏ/2 units is:
|Sx11 Sx12|
|Sx21 Sx22|
That is:
|0 1|
|1 0|
For a similar calculation, we have:
Sy11 = <0|Sy|0> =
<0|(1/2i)(S+ - S-)|0> = (1/2i)<0|S+|0> - (1/2)<0|S-|0>
(1/i)<1|S+|1> + (1/2i)<1|S-|1> = 0 - 0 = 0
Sy22 = <1|Sy|1> =
<1|(1/2i)(S+ - S-)|1> = (1/2i)<1|S+|1> - (1/2i)<1|S-|1>
(1/2i)<1|S+|1> - (1/2i)<1|S-|1> = 0 - 0 = 0
Sy12 = <0|Sy|1> =
<0|(1/2)(S+ - S-)|1> = (1/2)<0|S+|1> - (1/2)<0|S-|1>
(1/2i)<0|S+|1> - (1/2i)<0|S-|1> =ℏ/2i - 0 = - i ℏ/2
Sy21 = <1|Sy|0> =
<1|(1/2i)(S+ - S-)|0> = (1/2i)<1|S+|0> - (1/2i)<1|S-|0>
(1/2i)<1|S+|1> -(1/2i)<1|S-|1> = 0 - ℏ/2i = +i ℏ/2i
The matrix for Sy in ℏ/2 units is:
|Sy11 Sy12|
|Sy21 Sy22|
That is:
|0 -i|
|i 0|
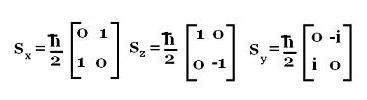
|
|