Coding &
programming
Installing CodeBlocs compiler
C language
C++ language
© The scientific sentence. 1998-2016
| |
|
Programming with C/C++ Language
I/O files
Using fstream classes
1. Definitions
File I/O is reading from and writing to files. We are going to hse
text files, that is, files that are composed only of ASCII text.
C++ has two basic classes to handle files, ifstream and ofstream. To use them, we include the header file fstream.
Ifstream handles file input (reading from files), and ofstream handles file output (writing to files). The way to declare an instance of the ifstream or ofstream class is:
ifstream a_file;
or
ifstream a_file ("filename");
ofstream a_file;
or
ofstream a_file ("filename");
The constructor for both classes will actually open the file if
we pass the name as an argument: example:
ifstream b_file ( "example.txt" );
// Opens for reading the file.
As well, both classes have an open command (a_file.open()) and a
close command (a_file.close()).
We aren't required to use the close command as it will automatically be called when the program terminates. But if we need to close the file long before the program ends, it is useful.
We know that C++ supports overloading operators, it is then possible
to use << and >> in front of the instance of the class as if it were cout or cin.
In fact, file streams can be used exactly the same as cout and cin after they are opened.
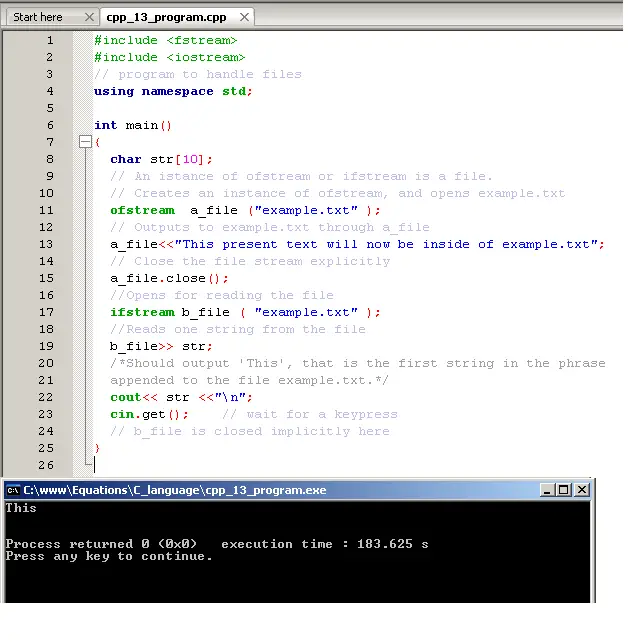
2.Example
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[10];
// An istance of ofstream or ifstream is a file.
// Creates an instance of ofstream, and opens example.txt
ofstream a_file ("example.txt" );
// Outputs to example.txt through a_file
a_file<<"This present text will now be inside of example.txt";
// Close the file stream explicitly
a_file.close();
//Opens for reading the file
ifstream b_file ( "example.txt" );
//Reads one string from the file
b_file>> str;
//Should output the following
cout<< str <<"\n";
cin.get(); // wait for a keypress
// b_file is closed implicitly here
}
Using CodeBlocs:
3. Operations within a file
The default mode for opening a file with ofstream's constructor is to create it if it does not exist, or delete everything in it if something does exist in it.
If necessary, you can give a second argument that specifies how the file should be handled. They are listed below:
ios::app -- Append to the file
ios::ate -- Set the current position to the end
ios::trunc -- Delete everything in the file
For example:
ofstream a_file ( "test.txt", ios::app );
This will open the file without destroying the current contents and allow you to
append new data.
When opening files, be very careful not to use them if the file could not be opened. This can be tested:
ifstream a_file ( "example.txt" );
if ( !a_file.is_open() ) {
// The file could not be opened
}
else {
// Safely use the file stream
}
|
|