Programming with C/C++ Language
Pointers, Arrays and Strings
Structures in C++
1. Structures

When our interest for an object ,as an orange, is only for its mass, it will
be sufficient to define the variable mass as well as its value.
int mass = 67;
Now if we may deal with the mass, the size, and the price or the color of an object, as an
ORANGE, it is useful to put all these variable on one variable
called the structure.
Structures are a way of storing many different values in variables
of potentially different types under the same name. Its design makes things more compact.
Structs are generally useful whenever a lot of data needs
to be grouped together as the struct ORANGE.
Here is the format for defining a structure:
struct ORANGE {
int mass;
float size;
int price;
char color;
};
ORANGE is the name of the entire type of structure
The variables within the struct are its elements.
To actually create a single structure as an instance,
the syntax is:
struct NAME_STRUCTURE {
the elements ..
};
struct NAME_STRUCTURE name_of_single_structure;
To access a variable of the structure it goes :
name_of_single_structure.name_of_variable;
Example:
struct ORANGE orange1; // compact variable
orange1 • size = 5.7; // we acess un element by the dot point.
2. Example program with structure
Here is an example program, the struct ORANGE with four variables in it.
struct ORANGE{
int mass;
float size;
int price;
char color;
};
int main()
{
ORANGE orange1; //orange1 is now an orange variable
//that has modifiable variables inside it.
orange1.mass = 200;
orange1.size = 6.5;
orange1.color = 'red';
orange1.price = 2;
}
ORANGE is a variable type like int, float , or char.
We can then create an orange with the ORANGE type. We can also return structures
from functions by defining their return type as a structure type. For instance:
ORANGE the_function();
3. Structures and pointers
To access the information stored inside the structure that is pointed to
by a ponter, we use the -> operator in place of the • operator.
All points about pointers still apply. Here is an example:
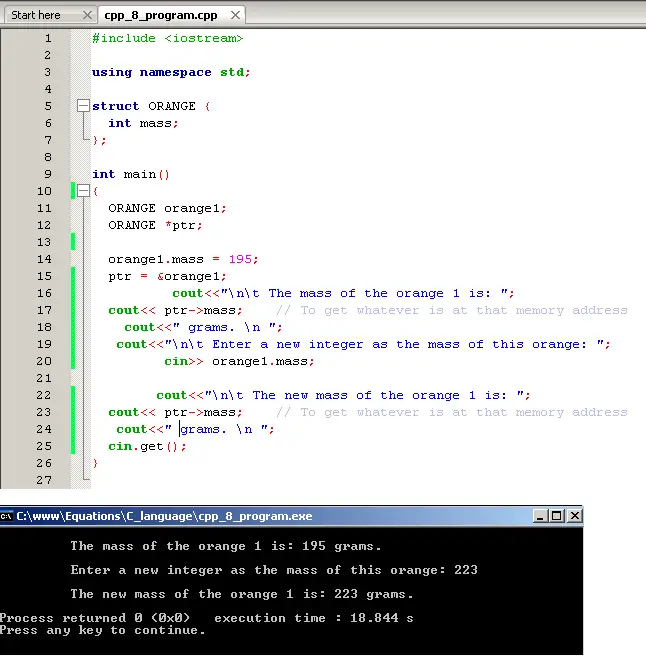
#include
using namespace std;
struct ORANGE {
int mass;
};
int main()
{
ORANGE orange1;
ORANGE *ptr;
orange1.mass = 195;
ptr = &orange1;
cout<<"\n\t The mass of the orange 1 is: ";
cout<< ptr->mass; // To get whatever is at that memory address
cout<<" grams. \n ";
cout<<"\n\t Enter a new integer as the mass of this orange: ";
cin>> orange1.mass;
cout<<"\n\t The new mass of the orange 1 is: ";
cout<< ptr->mass; // To get whatever is at that memory address
cout<<" grams. \n ";
cin.get();
}
Using CodeBlocs, we have:
|