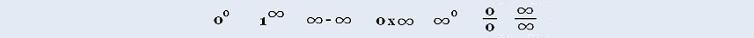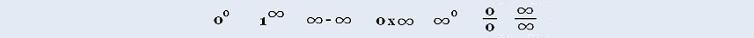Calculus I: Trigonometric functions
Limits & continuity
1. Limit of Trigonometric functions
1.1. Definitions
1.
If
lim f(x) = b (a is real or infinite, and b real)
x → a
Then
a)
| lim sin f(x) | = sin [lim f(x)] = sin b |
| x → a | x → a |
b)
| lim cos f(x) | = cos [lim f(x)] = cos b |
| x → a | x → a |
2.
If
lim f(x) = ± ∞ (a is real or infinite)
x → a
Then
a)
| lim sin f(x) |  |
| x → a | |
b)
| lim cos f(x) |  |
| x → a | |
1.2. Two particular cases:
lim (sin x)/x = 1
x → 0
Proof: see Exercises section.
lim (cos x - 1)/x = 0
x → 0
Proof: see Examples section.
1.3. Examples
a)
lim sin (3x) = 0
x → 0
b)
lim cos (3x/(x + 1)) = cos 3
x → + ∞
c)
lim tg (2x) = tg (π) = 0
x → + π/2
d)
lim cos (2x) 
x → + ∞
e)
lim sin(x)/x = ?
x → + ∞
lim sin(x)/x =  /∞ : ambiguous! /∞ : ambiguous!
x → + ∞
Remark that
lim sin(x) = real number in the interval [- 1 , + 1]
x → + ∞
Since
lim 1/x = 0
x → + ∞
We find:
lim sin(x)/x = 0 x real number in the interval [- 1 , + 1] = 0
x → + ∞
lim sin(x)/x = 0
x → + ∞
lim sin(x)/x = 0
x → + ∞
f)
f(x) = sin3(x)/5x3
lim sin3(x)/5x3
x → + ∞
=
(1/5) lim [sin(x)/x]3 = (1/5) (1)3 = 1/5
x → + ∞
g)
f(x) = ((cos x) - 1)/x
lim ((cos x) - 1)/x = 0/0: undetermined
x → 0
We have:
((cos x) - 1)/x = ((cos x) + 1)((cos x) - 1)/x ((cos x) + 1) =
((cos2 x) - 1)/x ((cos x) + 1) =
(- sin2 x)/x ((cos x) + 1) =
- (sin x)/x . (sin x)/((cos x) + 1)
Therefore:
lim ((cos x) - 1)/x
x → 0
=
lim [- (sin x)/x . (sin x)/((cos x) + 1)] = (- 1). (0/2) = 0
x → 0
lim ((cos x) - 1)/x = 0
x → 0
2. Continuity of trigonometric functions
2.1. Definitions
The two functions sin(x) and cos(x) are
continuous on R = ]- ∞, + ∞[.
If a function g(x) is continuous on an interval I, then
the function f(x) = sin g(x), and f(x) = cos g(x)
are continuous on the interval I.
2.2. Examples
Define the continuity of the following functions:
a)
f(x) = cos (x - 1)1/2
The domain of the function g(x) = (x - 1)1/2 is
I = ]1, + ∞[. So g(x) is continuous on the interval I,
so does the function f(x).
b)
f(x) = tan(x) = sin x/cos x
f(x) is discontinuous for the values of x such
as cos x = 0:
x = ± (2 k + 1)π/2
k is an integer.
3. Exercises
3.1. Exercise 1: (sin x)/x
f(x) = (sin x)/x
lim (sin x)/x = 0/0 : Undetermined
x → 0
Use a calculator in MODE radian, and fill in
the following two tables to find:
lim (sin x)/x = 1
x → 0+
and
lim (sin x)/x = 1
x → 0-
1. x approaches 0 from the left:
| x → 0- | f(x) |
| - 1 | 0.8414 |
| - 0.5 | 0.9588 |
| - 0.1 | 0.9983 |
| - 0.05 | 0.9995 |
| - 0.001 | 0.99999 |
2. x approaches 0 from the right:
| 0+ → x | f(x) |
| 1 | 0.8414 |
| 0.5 | 0.9588 |
| 0.1 | 0.9983 |
| 0.05 | 0.9995 |
| 0.001 | 0.99999 |
Conclude that:
lim (sin x)/x = 1
x → 0
3.2. Exercise 2: sin(3x)/tan(4x)
f(x) = sin(3x)/tan(4x)
We want to evaluate:
lim f(x) = sin(3x)/tan(4x)
x → 0
The value of 0 is: f(0) = 0/0 which is undetermined.
We have:
sin(3x) = sin(4x - x) = sin(4x) cos(x) - cos(4x) sin(x)
We know also: tan(4x) = sin(4x)/cos(4x)
We obtain f(x) =
(sin(4x) cos(x) - cos(4x) sin(x))/(sin(4x)/cos(4x)) =
cos(4x)) x [cos(x) - (cos(4x) sin(x))/sin(4x)]
We know also:
sin(4x) = 2 sin(2x) cos(2x) = 4 sin(x) cos(x) cos (2x).
So
f(x) = cos(4x) [cos(x) - cos(4x)/4 cos(x) cos(2x)]
Then
lim f(x) = lim {cos(4x) [cos(x) - cos(4x)/4 cos(x) cos(2x)]} = 1 [1 - 1/4] = 3/4.
x → 0
lim sin(3x)/tan(4x) = 3/4.
x → 0
|