Calculus III
Contents
3 Dimensional space
Partial derivatives
Multiple integrals
Vector Functions
Line integrals
Surface integrals
Vector operators
Applications
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
|
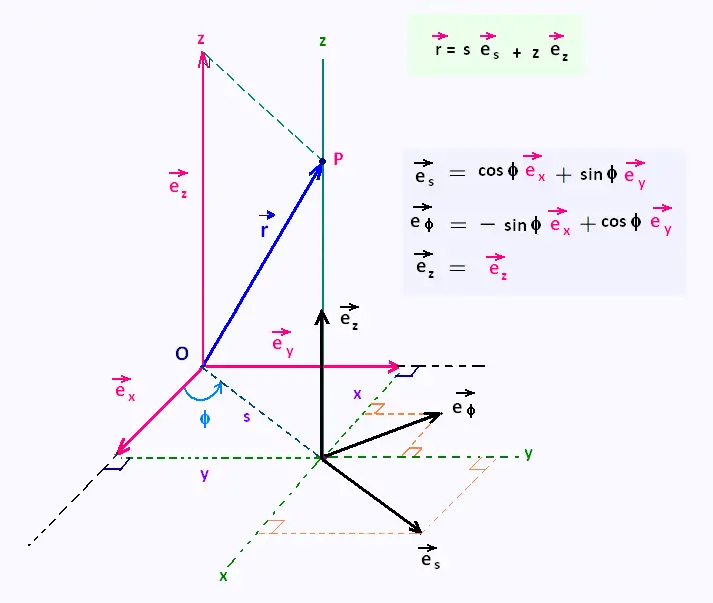
CYLINDRICAL COORDINATES
1. The basic relationships
The coordinates of a vector 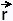 are the
coordinates of its associated point P. are the
coordinates of its associated point P.
The cartesian coordinates of a
point P are x, y and z.
The relationships btween cartesian coordinates and cylindrical coordinates
for a point P are:
x = s cos φ
y = s sin φ
z = z
x2 = x2 + y2
The folowing figure shows how to transform units vectors:
2. The cross product
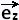 x x 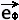
The components of the two vectors are:
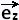 = 〈 0, 0, 1 〉 = 〈 0, 0, 1 〉
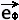 = 〈 - sin φ, cos φ, 0 〉 = 〈 - sin φ, cos φ, 0 〉
Then
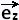 x x 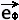 =
〈 - cos φ, - sin φ, 0 〉 =
- cos φ =
〈 - cos φ, - sin φ, 0 〉 =
- cos φ - sin φ - sin φ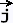
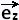 x x 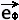 =
- cos φ =
- cos φ - sin φ - sin φ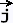
|
|