|
Electrostatics
Electromagnetics
Electricity &
Magnetism
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
Electrostatics: Coulomb's law
1. Coulomb's law
|
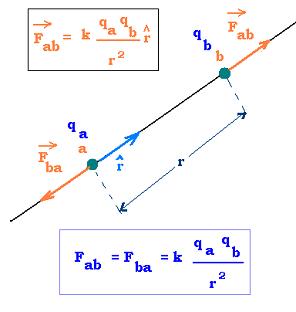
The electric force on the two stationary charges, qa and qb,
distant by r, is given by the Coulomb's law:
The constant εo is called the permittivity of free space
or vaccum.
The forces in the figure are oriented according to
Newton's third law. Here the charges are of like sign.
|
2. Example: Three points charges
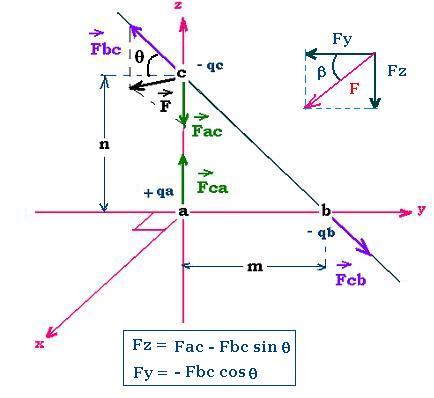
We want to calculate the Coulomb forces at the point c of charge - qc.
The charge on the point a is positive and the charge on
the point c is negative, so the related forces are attractive.
Fac = Fca = k qa qc/n2.
Fac has no components on the y-axis.
The charge on the point b is negative and the charge
on the point c is negative, so the related forces
are repulsive.
Fbc = Fcb = k qb qc/(n2 + m2)
Fbc has two components: one on the y-axis, and the
other on the z-axis.
The components of Fbc:
Fbc-y = Fbc cos(π - θ) = - Fbc cos θ
Fbc-z = + Fbc sin θ
Finally, the components of the
net force F on c are:
Fy = - Fbc cos θ
Fz = - Fac + Fbc sin θ
cos θ = m/[m2 + n2]1/2
sin θ = n/[m2 + n2]1/2
F = [Fy 2 + Fz2]1/2
tg (β) = Fz/Fy
qa = + 1 µC
qb = - 2 µC
qc = - 3 µC
m = 4.0 m
n = 3.0 m
k = 9 x 109 N.m2 /C2
Therefore
Fbc = k qb qc/(n2 + m2)
= 9 x 109 (2 x 10-6) (3 x 10-6) /25
= 2.16 x 10-3 N
Fac = k qa qc/n2
= 9 x 109 (1 x 10-6) (3 x 10-6) /9 =
3.0 x 10-3 N
cos θ = 3/5
sin θ = 4/5
Fy = - 2.16 x 10-3 (3/5) = - 1.30 x 10-3 N
Fz = - Fac + Fbc sin θ =
- 3.0 x 10-3N + 2.16 x 10-3 (4/5) N =
- 3.0 x 10-3N + 1.72 N =
- 1.18 x 10-3 N
F = [Fy 2 + Fz2]1/2 =
[1.69 + 1.4]1/2 x 10-3
= 1. 75 x 10-3 N
tg (β) = Fz/Fy = - 1.18 /(- 1.30) = + 0.91
β = 42o.
|
|