Statics
Contents
Applications
© The scientific sentence. 2010
| Statics
1. Massless string

A horizontal force F acts on a block A and moves it to
the left. The block B is connected to the block A by
a massless string. The whole system: "block A + string +
block B" moves to the left at an acceleration a.
The free body diagram for the string gives
according to Newton's second law:
TAonS - TBonS ms a
where ms is the mass of the string.
If the string is massless, then: ms = 0,
Therefore:
TAonS = TBonS (1)
According to the Newton's third law:
TAonS = TSonA (2), and
TBonS = TSonB (3)
Using (1), yields:
TSonA = TSonB
TSonA = TSonB
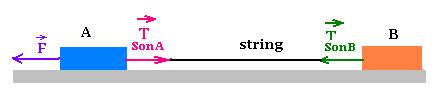
The two forces TAonS = TSonB
act as an action-reaction pair, and we can even omit the string.
If the string is massless, it can be omitted, and:
TSonA = TSonB
2. Example:

Let's consider two blocks A and B, connected
by a massless string, and pulled across a
frictionless table toward left by a force F exerted
toward left on A. We consider the mass of B is larger
than the mass of A. How about the tensions on the strings?
If the string is massless, then:
TBonA = TAonB
The net force of the system (two blocks + two strings)
is oriented to the left, therefore, the two blocks accelerate
to the left.
For the block blocks A, Newton's second
law is written as follows:
TFonA - TBonA = mA a
Therefore
TFonA = TBonA + mA a
and
TFonA > TBonA
For the block blocks B, Newton's second
law is written as follows:
TAonB = mB a
TFonA > TBonA
|
|