Optics: Images formed by refraction
1. Image of a point formed by refraction
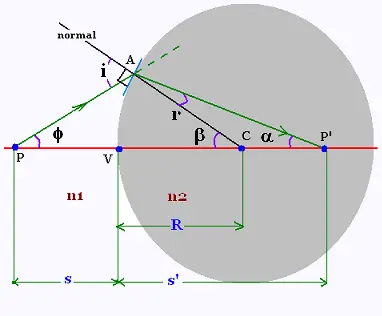
The paraxial ray PA refracts and becomes AP'.
All the related angles are small; then their
sin is equal to their measure radian. The Snell's law
is then written as: n1 i = n2 r
We have:
φ + β = i
β = r + α
n1 (φ + β ) = n2 (β - α)
(n2 - n1) β = n1 φ + n2 α
φ = AV/s
α = AV/s'
β = AV/R
(n2 - n1)/R = n1/s + n2/s'
(n2 - n1)/R = n1/s + n2/s'
(1)
2. Image of an object formed by refraction
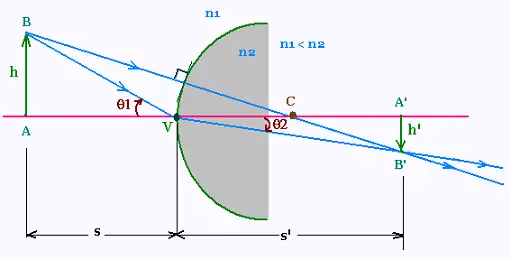
We want to know the lateral magnification m for the object AB
of image A'B' provided by the spherical surface.
We have:
tan θ1 = h/s, and tan θ2 = - h'/s'
For small angles, tan θ1 = sin θ1 ,
and tan θ2 = sin θ2 . Using the law of refraction:
n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2, we obtain:
n1 tan θ1 = n2 tan θ2
n1 (h/s) = n2 (-h'/s')
Therefore:
m = h'/h = - n1 s'/n2 s
Lateral magnification - Spherical refracting surface:
m = h'/h = - n1 s'/n2 s
(2)
3. Special case: Refraction by flat surface
In the particular case of a plane surace between
the two optical materials, the radius of curvature R is infinite.
The formula (1) is then written as:
(n2 - n1)/R = n1/s + n2/s' = 0
Therefore:
n1/s = - n2/s' , or
s'/s = - n2/n1
The formula (2) becomes:
h'/h = - n1 s'/n2 s = 1
The image formed by a plane refracting surface has
the same lateral size as the object.
Lateral magnification - Plane refracting surface:
m = h'/h = 1
Example:
Apparent depth under water
|