Mossbauer Effect
The Mossbauer effect involves the emission and absorption
of emitted gamma rays from the excited states of a nucleus.
Here is the what is about:
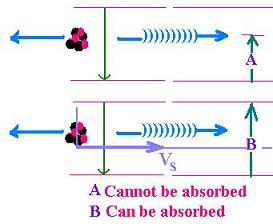 A nucleus is excited at a certain energy Ee,
It emits a gamma ray at energy Eg,
This emitted gamma ray has less energy than the available before
emission
The nucleus used the missing part of this energy to rcoil : Er
(about 1 eV for a 100 keV emitted photon)
The emitted radiation could not be absorbed by the identical atom,
because Eg is not equal to Ee.
The question is how to avoid the related recoil.
Mossbauer discovered that by placing emitting and absorbing
nuclei in a crystal, so that absorption was observed.
Commonly, Mossbauer Effect is experimented in Iron-57
of the 14.4 keV transition. The recoil energy can be calculated
from the momentum as follows:
A nucleus is excited at a certain energy Ee,
It emits a gamma ray at energy Eg,
This emitted gamma ray has less energy than the available before
emission
The nucleus used the missing part of this energy to rcoil : Er
(about 1 eV for a 100 keV emitted photon)
The emitted radiation could not be absorbed by the identical atom,
because Eg is not equal to Ee.
The question is how to avoid the related recoil.
Mossbauer discovered that by placing emitting and absorbing
nuclei in a crystal, so that absorption was observed.
Commonly, Mossbauer Effect is experimented in Iron-57
of the 14.4 keV transition. The recoil energy can be calculated
from the momentum as follows:
Er = (pc)2/2mc2
With :
pc = 14.4 keV
mc2 = 53.0 GeV
Er= 0.002 eV
WE will use the relativistic Doppler relationship:
Then n' - n = n V0/c
Er = h( n' - n) = h n V0/c = Ee V0/c
Thus :
V0 = cEr/Ee
V0 =3. 10 8. 0.002/14.4. 10 3
V0 = 43 m/s
The source moving with this velocity is
able to cancel the recoil energy and involve
then the related absorption.
|

