Pair Production
This process is related to a high-energy photon entirely
transformed into an electron and a positron as it is
represented in this reaction:
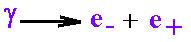
We are seeing a creation of two particled from a wave.
This latter wave must have an energy Eg, at least equal to the two
resting masses of electron and positron, that is 511 keV each. Thus,
the minimum photon energy required for pair production to occur is
1 022 MeV.
The mechanism is as follows:
Let's write:
Eg the photon incident energy,
Pg its linear momentum
Ee- the total energy of the produced electron
Pe- its linear momentum
Ee+ the total energy of the produced positron
Pe+ its linear momentum
The concervation of the momentum is:
Pg = P1 + P2 (1)
The horizontal projection gives:
pg= hN/c = p1cos a + p2 cos b (2)
The vertical projection gives:
p1 sin a = p2 sin b (3)
The concervation of the energy is:
Eg= Ee- + Ee+or E1 + E2 (4)
With :
E12 = p12c 2 +m02 c4 (5)
E2 2 = p22c 2 +m02 c4 (6)
We have then:
hN = (p22 c2 + m0 c4 )1/2 + (p22 c2 + m0 c4 )1/2 (7)
From (3) , The relationship (2) becomes`
hN/c = p1 cos a + p1 sin a cos b/sin b = p1 sin( a+b)/sin b
Thus:
p1 = (hN/c) sin b/ sin( a+b) (8)
And:
p2 = (hN/c) sin a/ sin ( a+b) (9)
The relation (4) becomes then:
hN = (p12c 2 +m02 c4)1/2 + ( p22c 2 +m02 c4)1/2
Substituing (8) and (9) in the latter equation, we can write it:
(((sin b)/sin (a+b))2+ (m0c2/hN)2)1/2 + (((sin a)/sin (a+b))2+ (m0c2/hN)2)1/2 = 1
We have used the available 3 equations and we have
4 unknown values ( p1, p2, a and b)
We get a relionship between a and b.
If we assume that p1= p2 , then a = b and E1= E2
we will get easily:
From ( 8) :
p1 = p2 = (hN/c)/ 2 cos a (10)
The inverse reaction to pair production is the annihilation reaction.
|

