Contents
The nucleus
Radioactivity
Radiation Measurements
Black body radiation
Statistical Mechanics
Radiation and scattering
Related topics
Related links
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
Radiation Physics: Preface
I. Medical Physics:

Medical Physics is the whole applications of the
Physics' principles in Medecine in order to diognose
and treat malignant desease. It includes mainly:
For scanning in Nuclear Medicine:
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
For diagnostic imaging:
X-rays (Radiology),
Ultrasounds, and
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
For Radiotherapy treatment:
Brachytherapy (HDR and LDR)
Ionizing radiation (Oncology)
II. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, that is the treatment of cancer, is done by
ionizing radiations like neutrons, electrons, γ-rays, and ions such as
protons. It is a palliative treatment, that the main goal is to kill cancer cells and shrink
tumors. It comes internally, that is Brachytherapy or Curietherapy.
and externally by using radiation beams from special machines, or from a particle accelrators.
We treat then cancer by protons.
But. why do we vafour Proton therapy?
Protons release most of their energy when they hit the tumor and deliver no
exit dose beyond the tumor boundary. Therefore, the dose of radiation conforms
to the tumor better and there is less damage to healthy tissue.
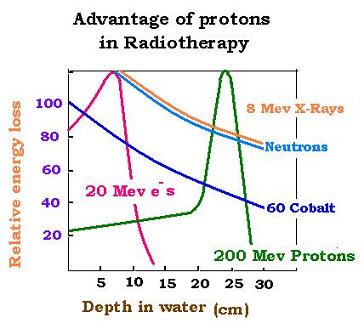
While standard particles such as electrons, neutrons, gamma-rays and X-rays used for
conventional treatments, lose their energy rapidly in tissues, protons have the major advantage over these conventional radiations to release their energy
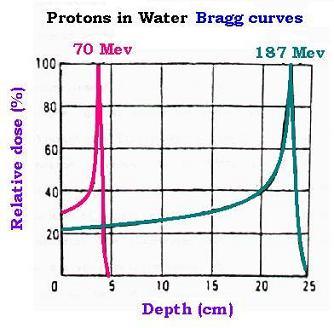
according to the Bragg peak. This advantage makes protons deliver a precise dose of energy directly to the tumour while reducing adverse effects to adjacent
normal tissues. By combining protons with different energies in a single beam, the Bragg peak can be modulated into a plateau that dumps a high dose of
radiation throughout the precise depth of the tumour.
|