A sigle wave
Superposition of waves
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
Dirac delta function
1. The general definition
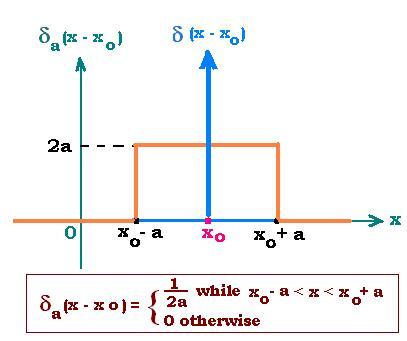
The general definition of this function is:
δa (x - xo) = 1/2a in [xo - a , xo + a] and zero otherwise.
δ (x - xo) = lim δa (x - xo)
a → 0
∫ f(x) δ(x - xo) dx = ∫ f(x) lim δa(x - xo) dx
a → 0
[- ∞, + ∞]
= lim ∫ f(x) δa(x - xo) dx
a → 0
[- ∞, + ∞]
= lim ∫ f(x) δa(x - xo) dx
a → 0
[xo - a, xo + a]
The variable x is now taken in the interval [xo - a, xo + a], then if a → 0 then x → xo.
Therefore:
∫ f(x) δ(x - xo) dx
= lim (1/2a) ∫ f(xo) dx = f(xo lim (1/2a) ∫ ) dx =
f(xo) lim (1/2a) [x] (between xo - a and xo + a)
a → 0
= f(xo) lim (1/2a) [(xo + a) - (xo - a)] =
f(xo) lim (1/2a) [2a] = f(xo). Therefore:
∫ f(x) δ(x - xo) dx = f(xo)
At the origin: xo = 0, we have the δ function &delta(x) such as:
∫ f(x) δ(x) dx = f(0).
2. Properties of the Dirac function
|
|
|