|
Applications
© The scientific sentence. 2010
|
Bisection method
for cables or bridges
/*This program "cable_strung.c" calls the function f(T) and
uses the bisection method to determine the tension in the cable.
Once this tension is computed, it is fixed as a parameter, like w and
ymin to compute the values of the height "y" with respect to the
position of the right hand pole "x". The related dvalues are
written in a file of type .csv that a Ms Excel spreadsheet
can open and graph.
The function f(T) is: y - ymin + T/w - (T/w) * cosh(w*x/T) is derived
from the double differential equation of the cable strung:
d2y/dx2 = (w/T)[1 + (dy/dx)2]1/2
For more info, link to : cable strung .
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
float x, y, ymin, w;
/*x is the distance from O to the right pole, y is the height
of the cable, ymin is the minimum height, and w is the uniform
weight w (in Newtons/meter) per unit length
y, x, and ymin : n meters. w in Newtons per meter
*/
// 1. Defining the fuction
//-----------------------------
// 1. 1. The fuction to compute T (in Newtons)
//----------------------------------------------
float f(float T)
{
double zz = w*x/T;
return y - ymin + T/w - (T/w) * cosh(zz) ;
//That is f(T) = 0
}
// 1. 1. The fuction to y with respect to x, once T is fixed
//-----------------------------------------------------------
float height(float x, float T)
{
double zz = w*x/T;
return (T/w) * cosh(zz) + ymin - T/w ;
//That is y
}
// 2. Main program:
//------------------
int main()
{
// 2 . 1. Input values:
//----------------------
printf("\n Input a value for y ");
printf("\n and for x in meters : --> ");
scanf("%f%f", &y, &x);
printf("\n Input values for w and ymin");
printf("\n w and ymin in meters : --> ");
scanf("%f%f", &w, &ymin);
/*Example:
------------
The inputs y=15,x = 50, ymin = 8 and w =8 are the
convenient values
*/
// 2. 2. Bisection method:
//----------------------------
// Finding the middle point ..
float l = 1, u = 3000, c[100];
// The tension T (in Newtons) is positive, start with 1,
//because zero leads to infinity
int i,n = 100;
float ss =0;
if(f(l)*f(u)<0)
{
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
c[i]=(l+u)/2;
if(f(l)*f(c[i])<0)
{
u=c[i];
}
if(f(l)*f(c[i])>0)
{
l=c[i];
}
}
// 2. 3. The results ( value of T):
//---------------------------------
printf("\nThe solution is T = %1.2f Newtons.\n",c[n]);
//Fixing the result T :
ss= c[n];
}
else
{
printf("There is no roots in this range .\n");
}
// 2. 4. Computing "y" with respect to "x"
//--------------------------------------------
/*
Filling in the two array "array_cable_x", and "array_cable_y"
The values of "x" and "y" respectively
*/
printf("\n");
/*printf("The heights, y, of the cable at each x:\n");*/
int count = -1;
float k, array_cable_x[101], array_cable_y[101];
for(k= -50; k<= +50; k++)
{
count = count +1;
//printf("\t %1.2f\n",height(k,ss));
array_cable_x [count]= k;
array_cable_y[count] = height(k,ss);
// Here "k" is x, and height(k,ss); is "y"
}
FILE *fp;
/* Writes the set of data values from array_cale to the
file "cable_array.csv":*/
fp = fopen("cable_arrays.csv", "w");
int j;
for (j=0;j<=100;j++)
{
fprintf(fp,"%1.2f,%1.2f\n", array_cable_x[j], array_cable_y[j]);
}
fclose (fp);
//The graph "y" vs "x" is given by MS Excel
return 0;
}
//---------- end ----------------------------------
--------------------------
Compiled with SciTE gives:
---------------------------
>gcc -msse2 -O3 -march=pentium4 -malign-double
-funroll-loops -pipe -fomit-frame-pointer -W -Wall
-o "cable_strung.exe" "cable_strung.c"
>Exit code: 0
---------------
Executed gives:
----------------
C:\CLanguage>cable_strung
Input a value for y
and for x in meters : --> 15 50
Input values for w and ymin
w and ymin in meters : --> 8 8
scanf("%f%f", &w, &ymin);
The solution is T = 1437.81 Newtons.
C:\CLanguage>
------------------------
Graph given by MS Excel:
------------------------
The file "cable_array.csv" is immediately created within
the same directory: C:\CLanguage>
The graph is the following where the increment is 5:
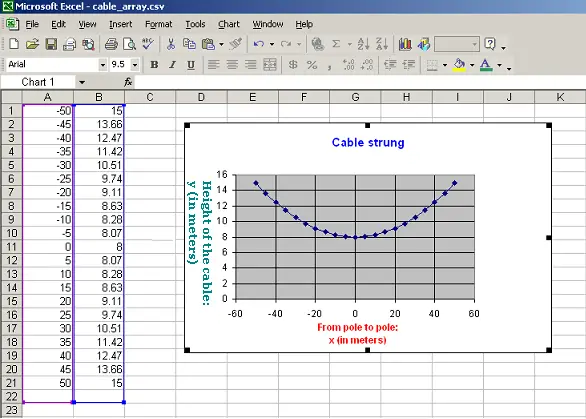
|
|
|