1. Preface
Java Remote Object Invocation allows a program to be execute a
remote function placed in a remote machine, side Server, from
a local machine, side client.In a remote machine we construct an
interface class and an implemented class that implements from the
first one. In a local machine, we construct a class client that
send a request towards the server.
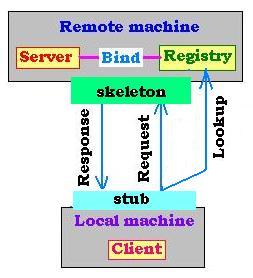
2. The system RMI
The mechanism is as follows:
- The server binds its name to the registry,
- The client looks up the server name via its the registry,
and establishes remote references,
- The client invokes a remote method in the remote server via
a socket.(in fact it's the stub's local machine that is responsible to marshal
parameters and forward data stream towards the server via the skeleton ),
- The server receives the request and invokes the object
implementation,
- The server sends a response to the client in the lical machine.
3. The steps to set the system
- Define the remote interface between the client and server objects,
- Implement this remote interface,
- Develop the client program,
- Compile the Java source files,
- Start the RMI registry.
- Start the remote server,
- Run the client
4. Example 1 Regards Applet
The related casses are the following:
Regards.java
RegardsImpl.java
RegardsApplet.java
1.First prompt:
set CLASSPATH = �C:\J2EE\RMI\Regards"
Compile:
C:\J2EE\RMI\Regards> javac Regards.java
C:\J2EE\RMI\Regards> javac RegardsImpl.java
C:\J2EE\RMI\Regards> javac RegardsApplet.java
Run:
C:\J2EE\RMI\Regards> start rmiregistry
C:\J2EE\RMI\Regards> java -Djava.security.policy=policy.all rmiServerImpl
2.Second prompt:
set CLASSPATH = �C:\J2EE\RMI\Regards"
C:\J2EE\RMI\Regards> Appletviewer RegardsApplet
The related applet is:
RegardsApplet
5. Example 2 Remote calculus
The related casses are the following:
rmiServer.java
rmiServerImpl.java
rmiClient.java
1.First prompt:
set CLASSPATH = �C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation"
Compile:
C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation> javac rmiServer.java
C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation> javac rmiServerImpl.java
C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation> rmic rmiServerImpl
C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation> javac rmiClient.java
Run:
C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation> start rmiregistry
C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation> java -Djava.security.policy=policy.all rmiServerImpl
2.Second prompt:
set CLASSPATH = �C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation"
C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation> java -Djava.security.policy=policy.all rmiClient
The rmic compiler has generated rmiServerImpl_Stub.class.
The Java -D= option set a system property.
The command line: C:\J2EE\RMI\Operation> start rmiregistry could be
done from Java\bin directory (as C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.6.0_03\bin).
The result are:
1. Side Server, we have:
ll rmiServerImpl
The server is waiting ....
2. Side Client, we have:
ll rmiClient
The Security Manager is loaded ...
The remote object is got ..
(20 + 30)* 10 = 500
6. About Security policy
In a such file, we can allow are deny access to some
directories. In These two programs, we have used the
policy.all
to grant some necessary access.
We can also the Java\bin directory (as C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_03\bin)
and policytool.exe. If we give all permissions, the file we can save looks
like this:
/* AUTOMATICALLY GENERATED ON Sun Mar 02 13:26:44 EST 2008*/
/* DO NOT EDIT */
grant {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
In the Java lib directory (as C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.5.0_14\lib\security),
we find java.policy file where we can set permissions.
|